

What is ELF test?
Enhanced Liver Fibrosis (ELF) test is a routine blood test used to assess the severity of liver fibrosis. Liver fibrosis is the scarring process that represents the liver’s response to injury or disease. Chronic liver disease can lead to liver fibrosis, liver cancer and even death. Cirrhosis and liver cancer are now among the top 10 causes of death worldwide, and in many developed countries, liver disease is now one of the top five causes of death in middle-aged people4-7.
There are four main causes of liver fibrosis:
What is ELF score?
The ELF score combines three serum biomarkers, which enables the identification of quantifiable level of liver fibrosis upon correlation. Based on the measurement of three biomarkers, the ELF score determines the extent of liver damage1-3,12:
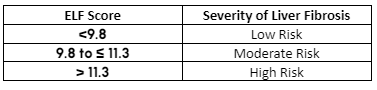
Generated with the three aforementioned biomarkers via the algorithm, the ELF score has been proven to correlate to the level of fibrosis as assessed by liver biopsy8-11. The spectrum of liver disease can range from simple steatosis, to cirrhosis and may be present for many years in the absence of abnormal liver function tests–mild to moderate liver fibrosis can exist without symptoms, which in itself supports its use for early detection and assessment.
How would the ELF test benefit patient?
Benefits of the test are as follows:
Reference